Protecting Children from Diarrhoeal Disease and foodborne Gastrointestinal infections
There are many factors that contribute to the continued incidence of Diarrhoeal Disease in young children, the most notable include consumption of unsafe water, and consumption of improperly cook or contaminated food. However experts predict that effective handwashing could reduce the numbers of children who die each day from diarrhoea by 50%[1]. With 760,000 children under 5 dying each year from diarrhoea[2], hand washing is the single most important hygiene step to prevent the spread of infectious diseases in young children.
Children should be encouraged to wash their hands from a very young age at home and at school and be taught to understand the impact of hand washing on their health.
Children should always wash their hands:
- Before eating or helping to prepare food
- After they have used the toilet or potty.
- After handling pets or other animals
- After playing outdoors or travelling on public transport
- When arriving home from school
- After coughing,sneezing or blowing the nose
Parents should take extra precautions around children including washing hands:
- Before preparing food for children
- After changing a nappy
- Before handling a baby
It is important for hands to be washed thoroughly to minimise the spread of germs:
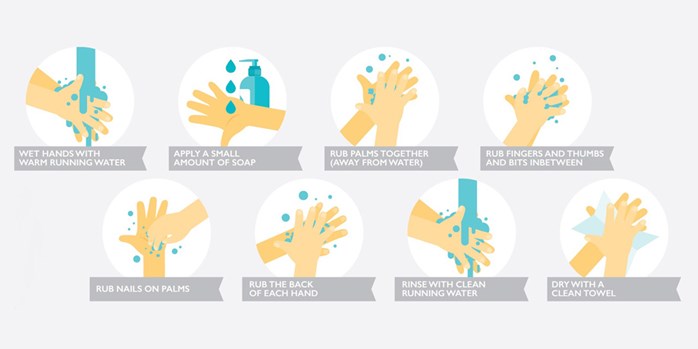
If soap and clean water are not readily available, an alcohol based hand sanitiser should be used. However, it the hands are dirty, they should always be washed. Use of hand sanitisers by children should be under adult supervision.
[1] World Health Organisation - Diarrhoea: why children are still dying and what can be done. Available at: http://www.who.int/maternal_child_adolescent/documents/9789241598415/en/
[2] http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs330/en/
Protecting Children from Foodborne Gastrointestinal Infections
The micro-organisms that cause food-borne illness can be spread from raw meat and vegetables directly on to chopping boards, utensils, worktops and on to foods to be eaten by young children. As children are susceptible to gastrointestinal infections and stomach upsets through eating contaminated food it is essential to ensure that food is cooked and stored properly, and that preparation areas are kept hygienically clean. The following food preparation hygiene tips are important to protect children from gastrointestinal infections:
- Clean and disinfect food preparation areas and chopping boards with an appropriate antimicrobial product
- Regularly clean and disinfect areas where food is stored
- Always wash hands before and after preparing food
- Wash fruit and vegetables with clean running water
- Don’t let juices from raw meat drip onto other foods
